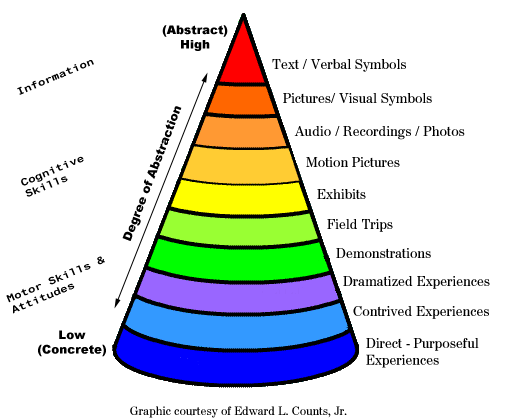
The Cone is a visual model, a pictorial device that presents bands of experience arranged according to degree of abstraction and not degree of difficulty. The farther you go from the bottom of the cone, the more abstract the experience become.
- Direct Purposeful Movement - First hand experience which serve as the foundation of our learning. We build up our reservoir of meaningful information and ideas through seeing, hearing, touching, tasting and and smelling.
- Contrived Experiences - In here we make use of a representative models or mock ups of reality for practical reasons.
- Dramatized Experiences - By dramatization, we can participate in a reconstructed experience, even though the original event is far removed from us in time.
- Demonstrations - It is visualized explanation of an important fact, Idea or process by the use of photographs, drawings, films, display, or guided motions.
- Study Trips - These are the excursions, educational trips, and visits conducted to observe an event that is unavailable within the classroom.
- Exhibits - These are displays to be seen by spectators. They may consist of working models arranged meaningfully or photographs with models, charts, and posters. Sometimes exhibits are "for your eyes only".
- Television and motion pictures - Television and motion pictures can reconstruct the reality of the past so effectively that we are made to feel we are there.
- Still pictures, recordings, radio - These are visual and auditory devices which may be used by an individual or a group.
- Visual Symbols - These are no longer realistic reproduction of physical things for these are highly abstract representations.
- Verbal Symbols - They are not like the objects or ideas for which they stand. They usually do not contain visual clues to their meaning.
APPLICATION
Harvard psychologist, Jerome S. Bruner, presents a three tiered model of learning where he points out that every area of knowledge can be presented and learned in three distinct steps.

It is highly recommended that a learner proceeds from the ENACTIVE to the ICONIC and only after to the SYMBOLIC.
Three pitfalls that we should avoid with regard to the use of the Cone of Experience:- Using medium in isolation
- Moving to the abstract without an adequate foundation of concrete experience
- Getting stuck in the concrete without moving to the abstract hampering the development of our students' higher thinking skills.

